The Rise of Intelligent In-Car Navigation: Design Lessons from China
February 24th, 2024 · Written by Samuel Jesse

Contents
Once a mere afterthought by drivers who simply mounted standalone devices to their dashboards, navigation technology has rapidly evolved into an integral part of the connected vehicle experience. Modern in-car navigation systems feature integrated mapping, live traffic feeds, route planning, and guidance delivered through vivid touch displays and conversational voice assistants.
While early navigation HMIs provided the basics of getting from point A to point B, today's systems tap cloud integration, predictions based on artificial intelligence, and an awareness of surrounding vehicles to offer safer, smoother, and more personalized journeys. Navigation is now fundamental to the very driving experience itself.
Modern navigation HMIs provide immense value - especially in expansive and highly urbanized megacities. Yet surprisingly, even some veteran automotive designers need to pay more attention to the importance of advanced mapping capabilities tailored for complex environments.
Even some HMI professionals from top European automakers question the need for details like real-time traffic alerts, predictive ETAs, and companion mobile apps integrated into navigation systems. Coming from smaller countries with less daunting roads, they might feel the basic directions suffice.
However, speak to designers immersed in the bustling Chinese mobility ecosystem, and cutting-edge navigational tech emerges as an absolute necessity. When navigating dense modern locales, enhancements like machine learning for personalized route planning, driver monitoring systems, and voice-guided augmentation are critical to the user experience.
At the bleeding edge of this navigation revolution sit Chinese automotive brands. Fueled by explosive growth in mobility demand amongst China's tech-fluent middle class, domestic marques like XPeng, Nio, Li Auto, and HiPhi drive progress in self-driving programs, augmented reality heads-up displays, and other advances that transform simple GPS into intelligent copilots.
Within China's thriving vehicle tech arena, evaluating, benchmarking, and drawing inspiration from sophisticated navigation HMIs is now essential for global automotive UX and interior designers alike. Understanding the leading edge of design from Beijing to Shanghai has become requisite research for industry professionals worldwide.
This piece will explore both seminal and still conceptual navigation tech that sets Chinese automakers apart. By examining key HMI components, UX considerations, use cases, and future trajectories, designers can grasp the possibilities of what navigation could become - and spark ideas for their own projects and infotainment systems ahead.
Key Components of Modern Navigation HMI
Visual Display Design
As in-vehicle navigation evolves from portable devices into integrated driving suites, the visual display remains central to the utility and usability of mapping and guidance. Contemporary navigation HMIs present far more visual information than before - using high-resolution graphics, augmented overlays, and dynamic traffic depictions. Understanding the expanding functional territory of the automotive navigation display empowers designers to craft more useful and intuitive implementations.
High-Resolution 3D Mapping
In-car navigation displays continue growing in terms of both proportions and imaging fidelity. Wide, ultra-high definition screens provide ample digital real estate to depict precise 3D renderings of cityscapes navigated by the vehicle. Lifelike representation of roads, buildings, foliage, and geographical contours boosts situational recognition for drivers. Designers must leverage added screen size and sharper imaging to showcase more navigation details versus older, abstracted 2D maps.
Augmented Reality Route Overlays
Visionary concepts from Chinese electric vehicle maker HiPhi point towards augmented reality windshield displays that integrate navigation guidance directly into the driver's field of view using intelligent projections. Similarly, chassis-mounted LiDAR sensors that perceive real-time environments could soon overlay ideal routing prompts onto actual pavement and landmarks seen through the windshield. Bringing digital mapping into the physical world promises to quicken reaction times and reduce the eyes-off-road duration.
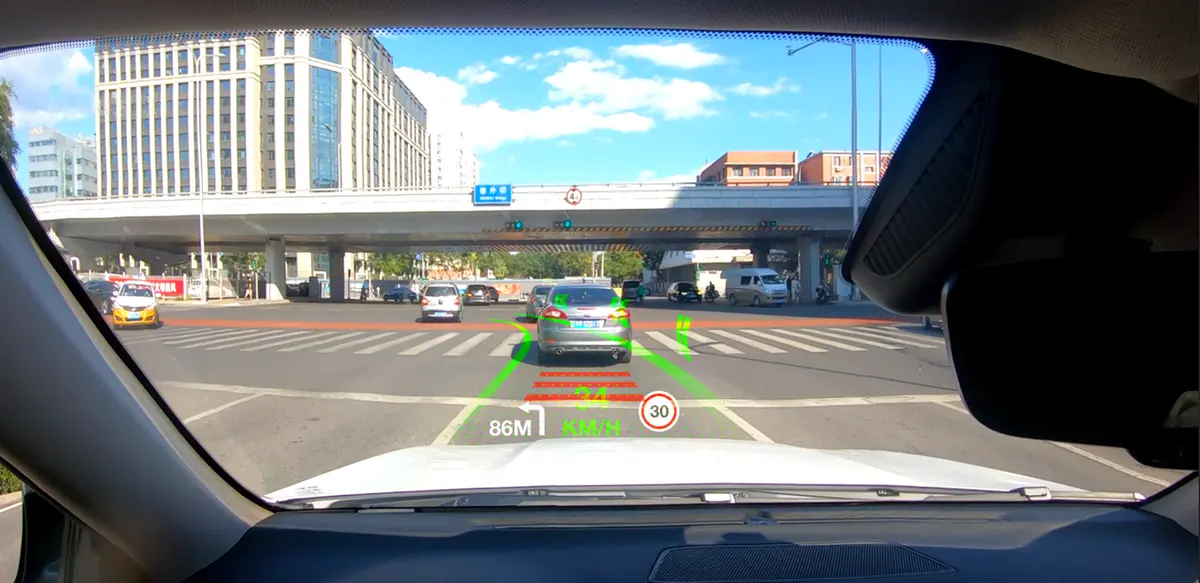
Dynamic Route and Traffic Visualization
As mapping platforms tap real-time data from transportation infrastructure and crowdsourced vehicle sensors, in-car navigation UIs can visualize live traffic, hazards, and dynamic ETAs. Instead of static maps, tomorrow's HMIs may showcase flowing visualizations that bring current roadway conditions to life. Vehicle sensor capabilities could also enable smarter lane guidance and junction warnings tailored to surrounding traffic detected by the car itself.
Gesture Control Integration
Touchscreens already allow drivers to manipulate navigation displays through direct input. But the next wave of HMIs could interpret simple hand motions without touching screens. Gestural interfaces reduce distractions when controlling map views, toggling info layers like traffic data, or even placing waypoints along a route. Chinese company Joynext plans to develop navigation systems that recognize common gestures as input mechanisms.
Voice-Based Navigation UX
Alongside touchscreens and gesture recognition, voice is a primary modality for modern automotive HMIs - including in-car navigation. Conversational assistants, nuanced speech input interpretation, and audio optimization make voice a versatile, hands-free control mechanism.
Conversational Voice Assistants
Voice-activated assistants like XPeng's "Little P" and Baidu's DuerOS platform tap natural language processing to enable relatively complex dialogue with navigation systems. Drivers can describe destinations, adjust route preferences, request pit stops, and use increasingly conversational commands. Future speech capabilities could mirror verbal exchanges between passengers to unlock more intuitive trip planning.
Natural Language Input
Similarly, interpreting natural speech allows navigation systems to support flexible turn-by-turn guidance adjustments. Using normal sentence formulations, drivers can reroute, add waypoints, or specify route aspects like avoiding highways and tolls. As cloud-connected speech comprehension evolves across consumer devices, cars can better decode nuanced voice instructions even amid road noise.
Personalization Based on Driver Profiles
Perfecting voice-based UX includes tuning to individuals' vocal patterns over time. As navigation systems recognize regular drivers via biometrics like bone conduction technology, HMI responses can be personalized, from adjusting guidance volume/pace to remembering frequent trips and suggesting alternative paths to work based on traffic data. Multi-occupant cars can also automatically identify speakers to understand verbal requests in context.
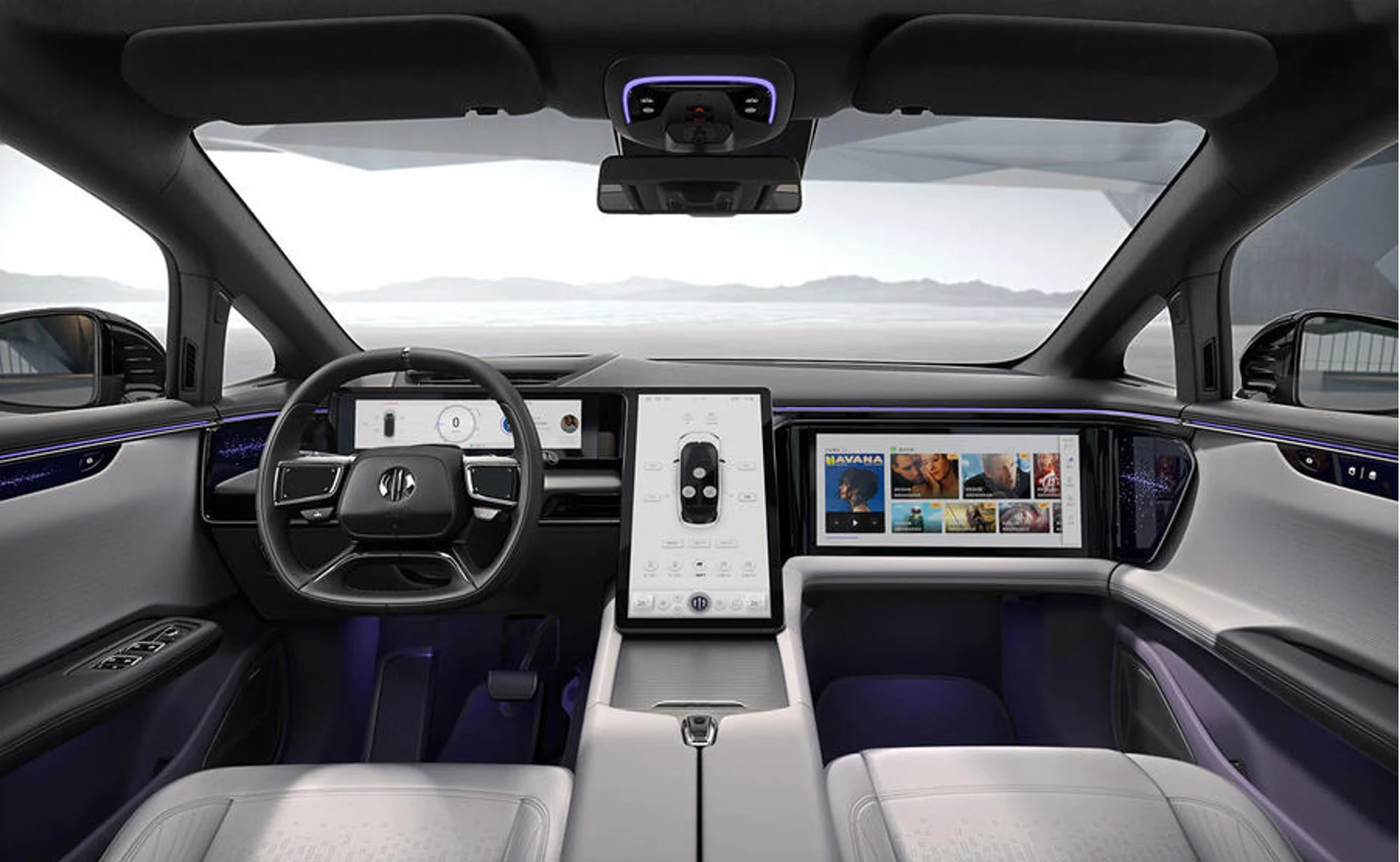

Integration with Cloud Platforms
As mapping platforms migrate to the cloud, in-car navigation can receive live updates on traffic, routing around incidents, discoverable points of interest, and other dynamic guidance. Without lag, cloud-hosted navigation means continuously updated ETAs and visualization of surrounding mobility flows. Offline fallback and reliable connection protocols remain vital, though.
Modern navigation relies heavily on wireless connectivity for real-time mapping data and deep integration with mobile ecosystems: cloud syncing, embedded travel apps, and cross-platform destination sharing highlight growing synergies.
Current automotive operating systems (AOS) platforms like CarPlay and Android Auto leverage external devices like smartphones. But AOS is evolving, integrating AI-derived technologies like computer vision, voice recognition, and natural language processing further. This will enable advanced multi-sensory interactions between cars, drivers, and occupants.
Traditional OEMs and tech giants like Baidu, Alibaba, and Huawei compete in the AOS market. Mercedes-Benz is investing heavily in AOS development, aiming to leverage it across models by 2024 and explore new revenue streams through software upgrades. Alibaba is pursuing an "AOS+Telematics" integration for a connected ecosystem.
Parking, Fueling, and Other Navigation Apps
China again leads the development of "light app" mini-programs designed explicitly for driving contexts. For instance, parking apps built into Tencent's WeScenario platform automatically surface when the vehicle nears destinations. Without installing standalone apps, pertinent parking, fueling, or charging point finders manifest when appropriate to simplify roadside stops.
Syncing Destinations Across Devices
Cross-device experiences allow drivers to set destinations from home and have guidance ready in the car's dashboard upon entry. Integrations like HiPhi's notification sync when approaching also help passengers prepare for upcoming maneuvers as riders transfer from other transit. Deeper hooks into mobile ecosystems promise more anticipation of driver needs.
Shared Waypoints for Group Travel
Finally, social-first Chinese consumers enjoy sharing trips through messaging apps like WeChat. Advanced navigation HMIs allow vehicle occupants to collaboratively add sequential waypoints to a journey visualized on the central touch display. Social planning integrations further optimization of routes involving multiple passengers.
Innovative Navigation Solutions in China
As advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) progress towards fully autonomous vehicles, sophisticated navigation served by augmented HMIs becomes mandatory. The pioneering work of Chinese companies makes clear that future self-driving depends on highly precise real-time mapping, adaptive human-machine dialogue, and tailoring route guidance to unpredictable factors.
XPeng's NGP City Pilot Program
Guangzhou-based XPeng's Navigation Guided Pilot (NGP) platform demonstrates autonomous city navigation that interprets complex environments. Using an array of LiDAR, radar, and camera inputs, NGP landmark detection and route mapping handle dense skyscrapers, unpredictable pedestrians, and congestion better than vision-reliant alternatives. Vehicle-infrastructure communication further enhances hazard perception and real-time course correction.
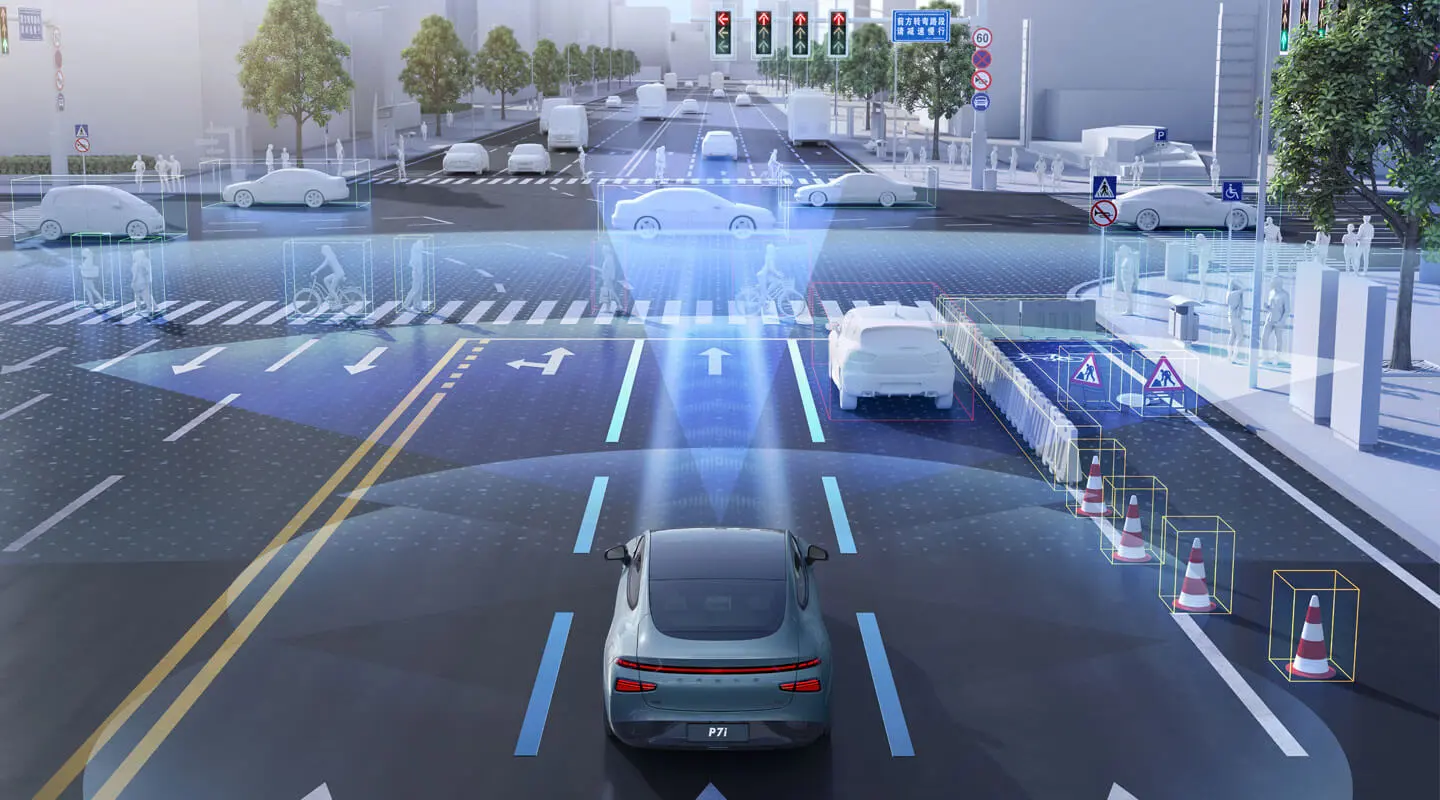

Huawei's Real-Time Mapping Capabilities
In partnership with navigation leader TomTom, Huawei supplies highly accurate maps to aid next-gen ADAS rollouts across China. Huawei's ADAN solution integrates sensors, cloud syncing, and software to attain centimeter-grade positioning data regarding landscapes, buildings, and roads. This mapping fidelity delivered in real-time allows vehicles like the ARCFOX αT to better position themselves against surrounds while driving autonomous modes.
Personalization and Prediction
Looking beyond self-driving, Chinese brands like Nio and XPeng also stretch innovation around tailoring guidance to individuals and predicting desired destinations. Personalized trip preferences and machine learning of behavioral patterns aim to enhance the humanness of navigation interactions.
Nio's NOMI System Learning Driver Behaviors
In vehicles like Nio's ET7 sedan, the NOMI assistant platform learns routing habits and patterns to offer smarter recommendations over time. By analyzing frequently driven routes, departure times, and past locations entered, NOMI can automatically set destinations, route around traffic, and enhance ETAs based on each driver's developing profile.

Prompt-Based Recommendations
Additionally, the NOMI system prompts drivers with suggested destinations based on the day, time, and other contextual signals. For instance, ask if the workplace should be routed to on Tuesday morning or suggest heading to the gym when typical workout patterns are observed. Basic IFTTT-style triggers help navigation feel more personalized.
User Profile Syncing Across Cars and Services
Nio's NOMI platform remains consistent when drivers upgrade vehicles or switch models, porting personalized experiences from one car to the next. Profile syncing allows navigation guidance to stay tailored to the individual rather than starting from scratch each lease cycle. Cross-platform profile unity promises more seamless navigation even in future autonomous robo-taxi scenarios.
Enhanced Safety Mechanisms
As rich mapping functionality and immersive displays amp up drivers' visual engagement with navigation systems, Chinese automakers prioritize safety. Integrating driver monitoring, expanding multimodal inputs, and promptly conveying warnings aim to secure route guidance.
Driver Monitoring Integration
Vehicle interiors from companies like Great Wall Motors and Geely incorporate inward-facing cameras for tracking driver attention levels on central touch displays. Computer vision algorithms assess gaze time on the navigation display relative to the road to model and prevent distraction risks. If visual engagement becomes unsafe, the system dashboard then surfaces prompts to reorient focus or enable vocal guidance.
Multimodal Inputs to Reduce Distraction
Enabling navigation adjustments via conversational speech, finger gestures, and haptic controls on the steering wheel or armrest allows drivers to modify routes without looking away from the road. Multimodal HMI adds more eyes-free manipulation so visual displays do not become all-consuming. Prioritizing tactile buttons for critical functions also helps.
Warning Systems and Machine Reflexes
Vehicles like the BYD Han EV and Nio's ET7 integrate automated emergency braking capabilities to halt sudden collisions. Still, the same reflex principles apply to fast-emerging hazards identified by navigation systems. If the route mapping detects a hazardous obstruction ahead not yet visible to the driver, audible and visual warnings deploy while the car proactively decelerates to prompt human response.
The Future of Automotive Navigation HMI
As autonomous driving, connectivity upgrades, and user experience expectations transform personal mobility, mapping, and guidance, HMIs will continue adapting in tandem. While the full extent of innovations remains unseen, precise UX trajectories emerge alongside new vehicle infrastructure possibilities.
Predictions on User Experience Shifts
Dominant changes are headed toward ambient displays, minimized driver distraction, and augmented visual immersion as early steps toward self-driving vehicles become common in traffic.
More Ambient, Heads-Up and Glanceable Displays
Interior concepts from Chinese startup Human Horizons highlight subtle ambient displays using projection mappings, holograms, and glanceable panels. These present navigation in the periphery, not as visual focal points. Similarly, AR overlays on windshields and total LIDAR-generated views require less direct staring. The route guidance experience aims to recede from constant attention.
Truly Conversational Voice Navigation
As speech comprehension advances, verbal exchanges with smart assistants promise truly conversational navigation queries rather than rigid command structures. Using AI and back-and-forth talk, route optimizations, and destination discussions could flow more naturally. Voice proves essential as manual controls phase out. Major AI players like Baidu and Alibaba are expanding their automotive AI capabilities through strategic partnerships. As the technology matures, AI adoption across the industry will grow.
AR Windshield Augmentation
Concepts from incumbents like Mercedes and startups like Nreal integrate small projectors or reflective optics inside vehicles to overlay navigation prompts directly onto the road ahead as visualized through the windshield. This augmented reality paradigm promises extremely low distraction guidance placed right onto the physical world.
Autonomous Driving Integration
China is aggressively pursuing autonomous driving, advancing from hands/eyes off temporarily to hands/eyes off capabilities. Full autonomy is targeted for 2025-2040. Leading OEMs are acquiring startups, forming alliances, and self-developing AD technologies. The "camera + radar + computer vision" solution pioneered by Tesla dominates.
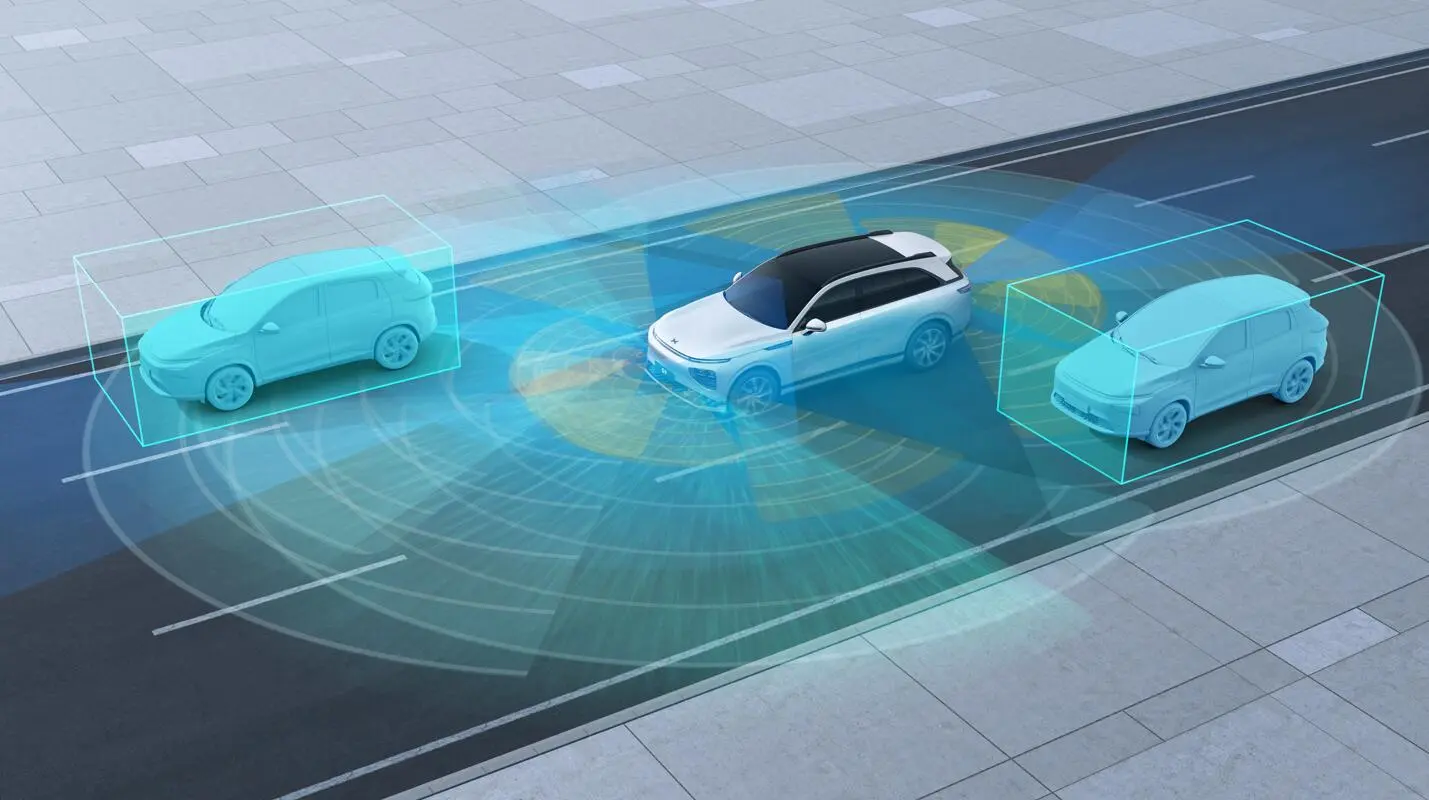
Integrating AD with HMI is critical for a seamless user experience. Advanced sensing, computing, and vehicle control systems are required. Centralizing the electrical/electronic architecture (E/EA) is vital for managing energy consumption. OEMs like Geely and Tesla are taking proactive steps in E/EA integration.
As the intelligence and capabilities of automotive navigation continue to advance, the in-car experience stands poised for revolution. Modern navigation HMIs in leading Chinese vehicles provide a glimpse into a dynamic future driven by immersive interfaces, predictive machine learning, and deep customization for each driver.
Yet, realizing this vision relies on designers worldwide learning from and collaborating with automotive innovators across China. By studying UX innovations, use case discoveries, and ADAS developments from Shanghai to Shenzhen, professionals worldwide can spark creative navigation concepts for their regions and projects.
The path ahead promises autonomous-ready vehicles where ambient interfaces and augmented visuals seamlessly guide passengers through complex megacities and winding terrain. The race towards this future begs the industry’s brightest minds to intently evaluate pioneering work on intelligent automotive HMI in China today.
The roadways of tomorrow begin with the interconnected blueprints drafted today. It is an exciting time for global designers to enrich their perspectives and toolsets by engaging with geography and defying the limits of modern navigation.
Have a project in mind?
Join our newsletter!
Get valuable insights on the latest digital trends, strategies, and developments in China and globally delivered straight to your inbox.